|

|
Health Foundation # 5:
Protect Your Mitochondria & Your Heart
The mitochondria are “the engines” or power generating organelles of the individual cells of the human body. They make us ”alive” and capable of doing the things we do. In this respect, the mitrochondria are similar to the engine of a car. They power us up... without them, we couldn’t live or do anything.
The cardiovascular system is also essential to the life of the body. It’s constant pumping action is like the constant rolling of a car’s tires, without which a car wouldn’t move. And, just like if the tires of your car were to experience a blow-out, so, too, if your cardiovascular system were to have a blowout (cardiovascular event), you would stop or crash and the result could be life-ending, or terrible.
|
|
|
|
These Two Key Components for Human Life Must Be Protected
- Mitochondria
- Cardiovascular System
Not taking care of the mitochondrial cellular engines and the cardiovascular system of your body has consequences similar to not taking care of your car’s engine and tires...
- Not taking care of your mitochondria will have a result like an engine meltdown.
- Not taking care of your cardiovascular system will have a result like a tire blowout.
So, the consequence of neglecting either of the above is that your ability to function in life will be seriously impaired.
First Key Concept:
Engines needs to be protected from heat buildup. That’s why automobile engines have specialized engine cooling systems such as radiators and oil pumps. That’s why our cellular mitochondrial engines have specialized mitochondrial antioxidants.
Our body’s mitochondrial engines produce free radicals inside the mitochondrial matrix at the rate of 100 quintillion free radicals per second (200,000 superoxide anion radicals per mitochondria per second). These free radicals are like heat in a car engine. They must be quenched (cooled) or they will destroy the mitochondria and continue on to damage other parts of the cell as well.
The main thing to do to protect mitochondria from free radical buildup is to to increase the levels of mitochondrial antioxidants. This is done by ensuring optimum levels of the four mitochondrial antioxidants: Super Oxide Dismutase, Catalase, Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Glutathione.
Second Key Concept:
Things that “wear” or experience friction must be protected and renewed. Automobile tires rub the road and lose tread through friction. That’s why we rotate tires to protect them from uneven wear and replace the tires periodically. The cardiovascular system is stretched and worn from the continuous pumping of blood. That’s why new endothelial cells (linings of arterial walls) must constantly be repaired and why the pumping action of the cardiovascular system needs to be coordinated.
The two main things to do to protect the cardiovascular system from “wear and tear” are to eat nutrients (so that the endothelial cells can be constantly repaired) and to ensure the production of nitric oxide, which coordinates the contraction and expansion of the arterial walls and instructs the repairing of the endothelial cells.
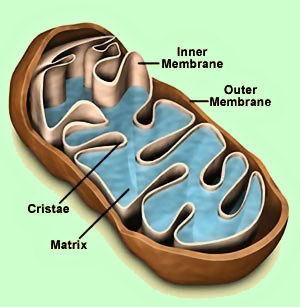 Protecting the Mitochondria Protecting the Mitochondria
There are actually quite a few things we can do to protect our mitochondria from free radical damage. Doing these things will enable you to get the “most miles” of out of your cellular engines (just like it’s possible to get 400,000 miles out of a car engine if you take care of it, possible to get only 60,000 miles out of an engine if you don’t take care of it):
Low Energy is the result of free radical buildup in the mitochondria. When the mitochondria sense a buildup of free radicals they will switch out of normal energy mode into low energy mode in order to protect themselves from free radical damage. In low energy mode no more free radicals are produced but also one fourth of the normal amount of energy is produced. This is the mode our bodies are in during deep sleep. With no free radical production, our cells can repair damage that occurred during the day through normal metabolism and from external toxins that enter our bodies.
The mitochondria’s switch over to low energy mode, not only occurs during sleep, but often occurs when we are awake, especially, as we get older, and free radicals have escalated and the mitochondria seek to protect themselves from more damage. That is why (when the mitochondria start to switch into low energy mode), we find that we must rest or sleep. If, instead, we use “will power” to go on functioning, we cause irreparable damage to our mitochondria.
# 1 - Be very picky about what you eat.
Food we eat gets processed by our mitochondria into useable energy... and the more we ”use” the mitochondria to convert food into energy, the more wear and tear on the mitochondria.
In other words, the seeds of our death are in the food we eat. So, a good practice is to ask yourself if the food you are about to eat is worth the mitochondrial deterioration that will result. Make sure your calories count by either enjoying those foods VERY MUCH or eating foods that come loaded with nutrients tools that will help preserve the mitochondria (or do both at once). In other words, eat nutrient dense food, as discussed in Health Foundation # 2.
# 2 - Eat less food at each meal
If you’re like most people, you have heard many times the concept that we should eat less; that we should leave the table hungry or eat very slowly so that our appetite thermostat has a chance to turn off before we over consume.
That was wise advice. Studies with animals show that eating half as much food can add 50 to 60 percent to maximum life span by limiting mitochondrial deterioration.
Learn more about the importance of eating less in in order to protect your mitochondria
# 3 - Supply your mitochondrial engines with “coolants” and “lubricants”
#4 - Remove Mitochondrial Toxins (Contaminants)
- Mercury (higher in those with amalgams and fish eaters)
- Aluminum (dietary for all)
- Arsenic (higher in smokers)
- Cadmium (higher in smokers)
- Lead
- Fluoride (water tx)
- Thallium
- Pesticides
- PCB (polychlorinated biphenyls) (multiple)
- Dioxin (multiple)
- PAH and PM (multiple compounds higher in smokers)
- Toluene, Benzene (in 91% & 96% of all persons)
- Trans fatty acids (in all diets except the very careful)
- Phthalates ( multiple)
Mercury is the worst of the above
48% of the mercury found inside cells is found inside the mitochondrial. Mercury in the mitochondria does the following:
- It causes severe oxidative damage leading to programmed cell death.
- It robs the mitochondria of glutathione, contributing to the mitochondria entering lower energy production mode.
Methods for removing mitochondrial toxins include:
- Zeolite
- Glutathione Enhancement
- EDTA Supplementation
# 5 - Fast Periodically
Scientists believe that during fasting hours is when the mitochondria repair themselves. The way to think about this, is similar to thinking about repairing a freeway. In order to do the repair work traffic, the freeway must be closed to traffic. In this case, the traffic is incoming food to be converted to energy. Two forms of fasting are most beneficial.
- Ensuring a daily fasting period of 12 to 13 hours - eight hours of sleep time plus three to four hours before going to sleep and one to two hours after waking up in the morning
- Engaging in water fasting of up to three days at a time
Cited Research and Father Study References:
Dr. Derek Huffman has also done research that shows that although exercise does prevent an early death, it does not increase maximum life span, which under eating does. Read more at http://www.medindia.net/news/Eating-Less-Extends-Life-Span-36725-1.htm
Only one non-transgenic intervention has been reliably shown to increase maximum life span and that is calorie restriction. Read more at: http://iangoddard.net/cr.htm
  A Cardiovascular Event is Like a Tire Blowout on the Freeway at 90 Miles An Hour - Scary and Often Deadly A Cardiovascular Event is Like a Tire Blowout on the Freeway at 90 Miles An Hour - Scary and Often Deadly
Strokes and heart attacks are life-changing, and often are life-ending events.
 Most heart attacks are the result of a build-up of plaque inside arteries. This build-up of plaque is the result of arterial endothelial cell (linings) damage, that occurs from free radical damage, which is ultimately the result of deficiencies and toxicities (i.e. life style). Most heart attacks are the result of a build-up of plaque inside arteries. This build-up of plaque is the result of arterial endothelial cell (linings) damage, that occurs from free radical damage, which is ultimately the result of deficiencies and toxicities (i.e. life style).
Thankfully, cardiovascular events are for the most part completely avoidable, due to the understanding gained from the Nobel prize winning research into the role of nitric oxide in perserving endothelial function (arterial wall linings) of being smooth and elastic. With high levels of nitric oxide in endothelial cells, the arterial walls do not develop plaque and blood pressure issues do not arise.
The single most important knowledge discovered to date in The amino acid known as arginine is the sole dietary source of nitric oxide the human body.
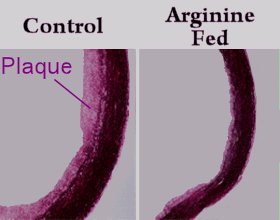 Our body converts arginine into nitric oxide. The pictures to the left show the results of an experiment where rabbits were fed a high cholesterol diet for 12 weeks. Half of the rabbits were also fed arginine, and half were maintained as controls. Pictures of their arteries were taken afterwards. The study concludes that “arginine completely blocked the progression of carotid intimal plaques, reduced aortic intimal thickening, and preserved endothelium-dependent vasodilator function.” Our body converts arginine into nitric oxide. The pictures to the left show the results of an experiment where rabbits were fed a high cholesterol diet for 12 weeks. Half of the rabbits were also fed arginine, and half were maintained as controls. Pictures of their arteries were taken afterwards. The study concludes that “arginine completely blocked the progression of carotid intimal plaques, reduced aortic intimal thickening, and preserved endothelium-dependent vasodilator function.”
From the Institute of Clinical Pharmacology (R.H.B., S.M.B.-B., L.P., M.B., J.C.F.) and Departments of Cardiology (R.P.B., A.M.) and Pathology (R.N.), Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Back to Top
|